promoting complex in the nervous system Biology Diagrams Key events in mitosis such as sister chromatid separation and subsequent inactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 are regulated by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. These events are mediated by the anaphase-promoting complex (APC), a cell cycle-regulated ubiquitin ligase that assembles multiubiquitin chains on regulatory proteins such as securin and cyclins and thereby targets them for

The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is a large E3 ligase that mediates ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of cell cycle regulatory proteins to control various events during replication

Control of mitotic transitions by the anaphase Biology Diagrams
The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is a ubiquitin ligase that has essential functions in and outside the eukaryotic cell cycle. It is the most complex molecular machine that is known

The anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) is an unusually large multi-subunit cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that functions to regulate progression through, and exit from, the mitotic phase of the cell cycle and controls entry into the S phase ([1 Anaphase-promoting complex (also called the cyclosome or APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11-13 subunit proteins, including a cullin and RING subunit much like SCF. Other parts
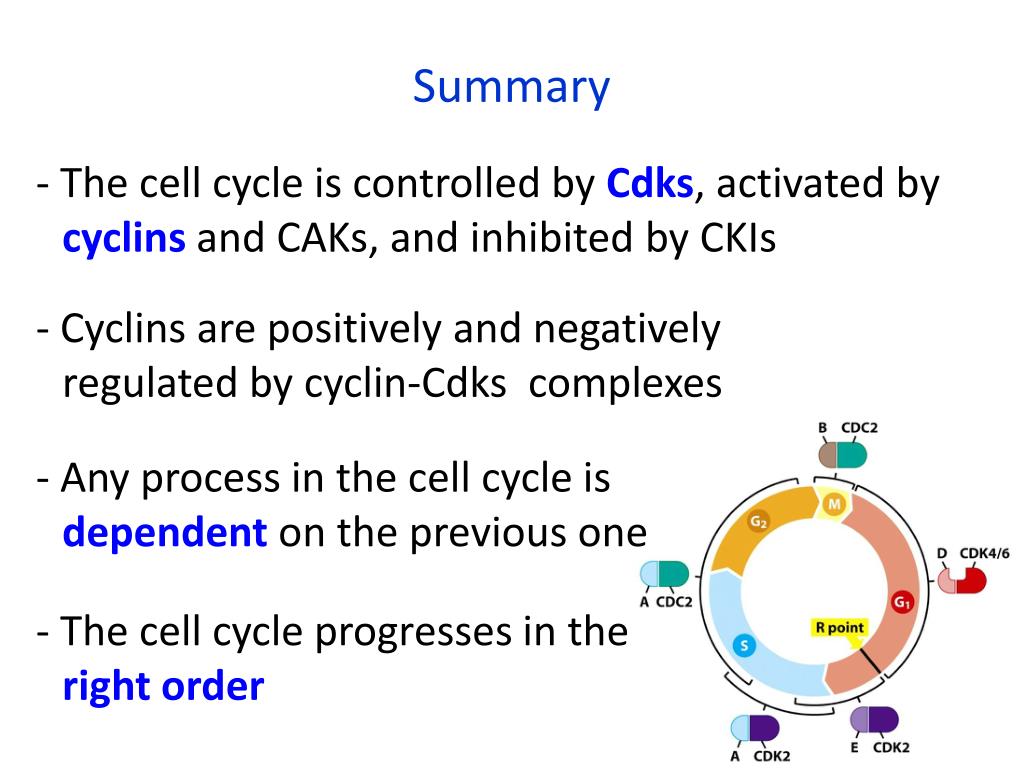
The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed ... Biology Diagrams
The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that helps control chromosome separation and exit from mitosis in many different kinds of organisms, including yeast, flies, worms, and humans. This review represents a new perspective on the connection between APC/C subunit mutations and cancer. The complex nature of
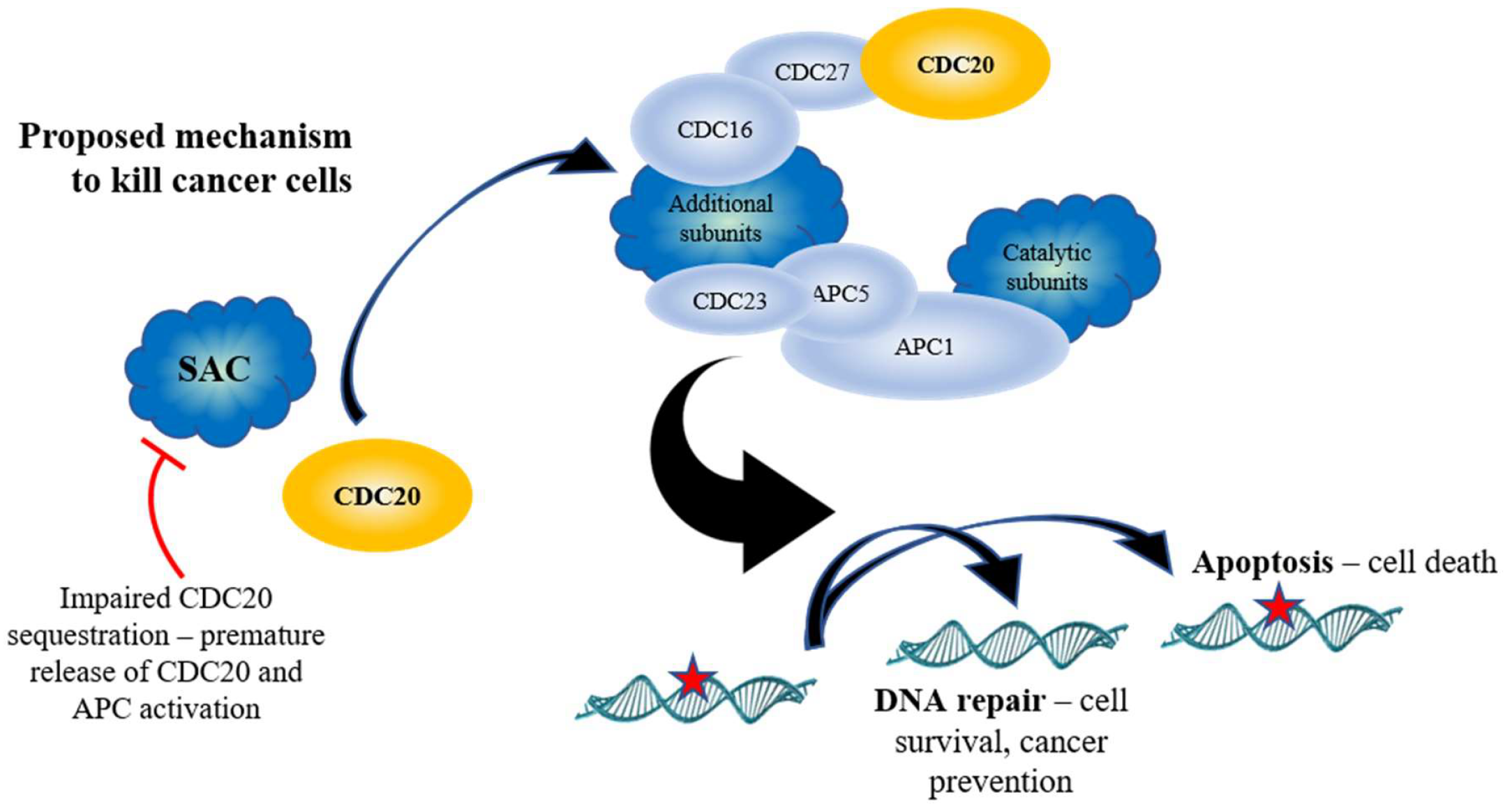
In mitosis, the activation of a large ubiquitin-protein ligase, the anaphase-promoting complex (APC), is required for anaphase initiation and for exit from mitosis. We show that APC is under complex control by a network of regulatory factors, CDC20, CDH1 and MAD2. CDC20 and CDH1 are activators of APC; they bind directly to APC and activate its 1. The anaphase promoting complex or cyclosome regulates cell cycle transitions. The anaphase promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) is a multi-subunit cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that functions to regulate progression through the mitotic phase of the cell cycle and to control entry into S phase [1-4].The APC/C also plays a role in regulating meiosis, and has been implicated in post
