RA Causes What are the Top Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Biology Diagrams The synovial membrane is soft and thin membrane yet has various significant roles that are very essentials for our body movements. Synovium (also called the synovial membrane) is a specialized connective soft-tissue membrane that lines the inner surface of synovial joint capsules. Together with bone, articular cartilage, tendon, ligament, and fibrous capsule, it is an important component of
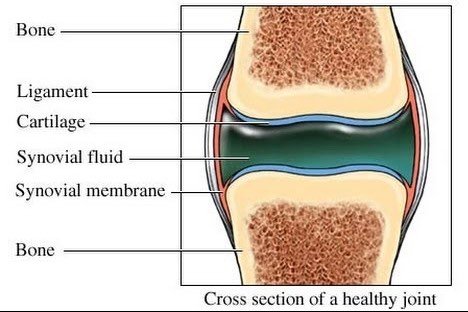
The inner layer (the intima) is thin and makes the synovial fluid that lubricates your joints. The outer layer (the subintimal layer) is made of a tough, fibrous layer of cells that protects the inner layer. It's flexible enough to move with your joint. The subintimal layer contains: Nerve cells. Lymphatic cells. Blood vessels. Synovial fluid

Synovial Fluid: Purpose and How to Increase It Biology Diagrams
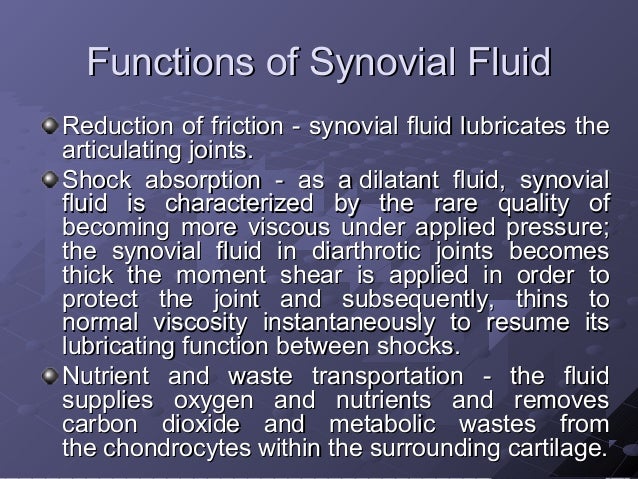
When your joints are not properly hydrated with synovial fluid, you can experience discomfort and inflammation. It was a wake-up call for me, as I realized the importance of keeping those joints well-oiled literally. Key Functions of Synovial Fluid 1. Lubrication. Let's first discuss the most obvious role of synovial fluid: lubrication. Synovial fluid is a thick fluid with an egg-white-like consistency that lubricates and reduces friction between joints. When synovial fluid is low, which tends to happen with age, it can contribute to joint stiffness and other aging-related joint conditions like osteoarthritis . Synovial fluid is a slippery fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints, such as the knees, elbows, and shoulders. Its primary purpose is to lubricate these joints, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement. Imagine the last time you were at the park, swinging your legs back and forth on a swing. That effortless motion? A lot of
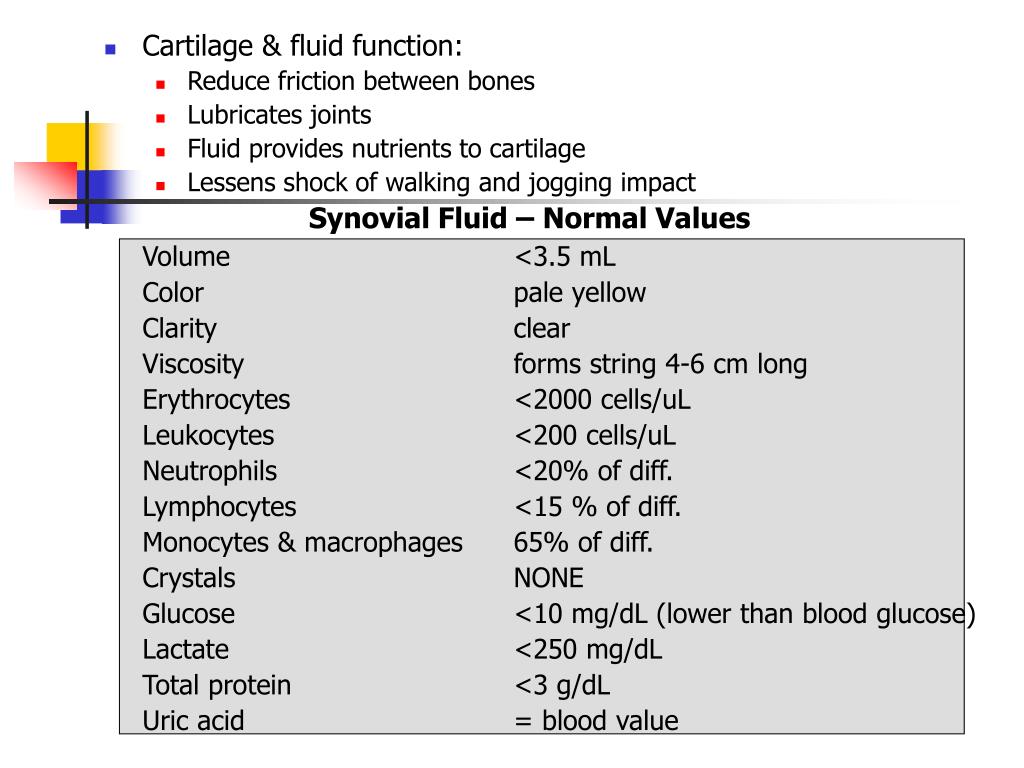
Synovial fluid plays an essential role in maintaining joint health. This viscous liquid is found in the cavities of synovial joints, which are the most common type of joint in the human body. It acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement. To optimize its movement and minimize friction, the human body produces synovial fluid within the joints. This article will delve into the physiology of synovial fluid, highlighting its composition, function, and significance. Synovial fluid is a viscoelastic substance found within synovial joints, such as the knee, hip, shoulder, and elbow.
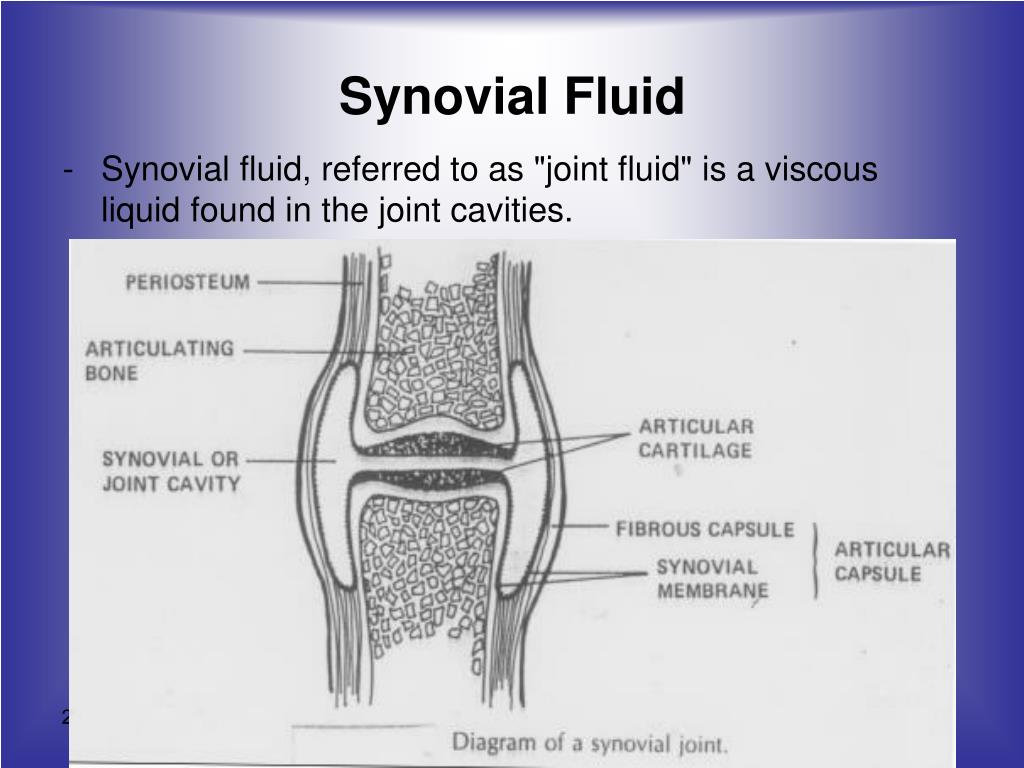
Synovium & Synovial Fluid Biology Diagrams
IntroductionThe human body is a complex system, and one of the key components that keep it running smoothly is the presence of various fluids. These fluids play critical roles, from transporting nutrients and oxygen to eliminating waste and protecting organs. Function: Synovial fluid lubricates joints, reducing friction between cartilage