The cohesin complex and its roles in chromosome biology Biology Diagrams Condensin and cohesin function in a number of processes independently of their classically defined roles, but the mechanisms that underlie these functions are poorly understood because disrupting either complex results in mitotic defects and lethality. Despite these hurdles, much has been learned through use of conditional, tissue-specific or Recent studies show that cohesin, condensin and their relatives are involved in a wide variety of chromosomal functions and their regulation, such as genomic imprinting, dosage compensation, and human congenital disorders [33, 44]. It is fascinating to investigate unidentified roles of cohesin and condensin during gametogenesis and early

Cohesin and condensin regulate cell cycle progression, ensuring chromatid cohesion and condensation and timing cell division. Cohesin's function in holding sister chromatids together is indispensable for the metaphase-anaphase transition, where its regulated cleavage allows synchronized chromatid segregation. Cohesin is a member of the SMC family of protein complexes which includes Condensin, MukBEF and SMC-ScpAB. Cohesin was separately discovered in budding yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) both by Douglas Koshland [1] and Kim [16] Other proteins modulate cohesin function by regulating this process, such as PDS5A, PDS5B, NIPBL and ESCO1 in

Cohesin and Condensin in Chromosome Architecture and Health Biology Diagrams
Cells deficient in condensin functions are not arrested at a specific stage of cell cycle, displaying chromosome segregation defects (i.e., anaphase bridges) and progressing through abnormal cytokinesis. Cohesin contains SMC1 and SMC3 and is involved in sister chromatid cohesion. The SMC5/6 complex contains SMC5 and SMC6 and is implicated Condensins are proteins of vital importance, playing a fundamental role in the structural and functional organization of chromosomes. This comprehensive review touches on aspects of condensin cell type- and tissue-specific functions, relevance to human disease, and insights gained from biochemical and structural analysis, providing a global view of condensin biology.
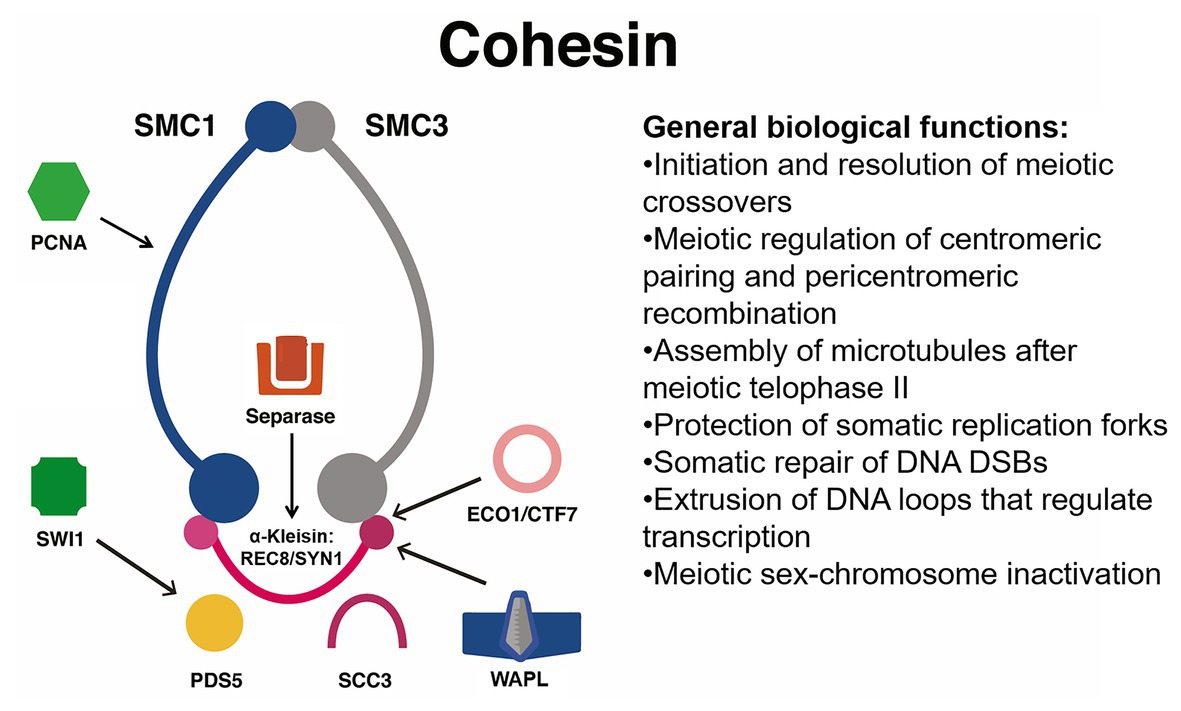
During the G1 phase, human chromosomal cohesin functions in a similar manner to condensin, engaging in interactions between neighbouring binding sites 107,108. Its chromosomal association is

Condensins: universal organizers of chromosomes with diverse functions ... Biology Diagrams
Condensin and cohesin complexes act in diverse nuclear processes in addition to their widely known roles in chromosome compaction and sister chromatid cohesion. Recent work has elucidated the contribution of condensin and cohesin to interphase genome organization, control of gene expression, metazoan development and meiosis. References 38, 43, 44, 50 and 51 provide intriguing suggestions for new roles of cohesin or condensin subunits in aspects of gene regulation, including silencing, chromatin insulator function and
